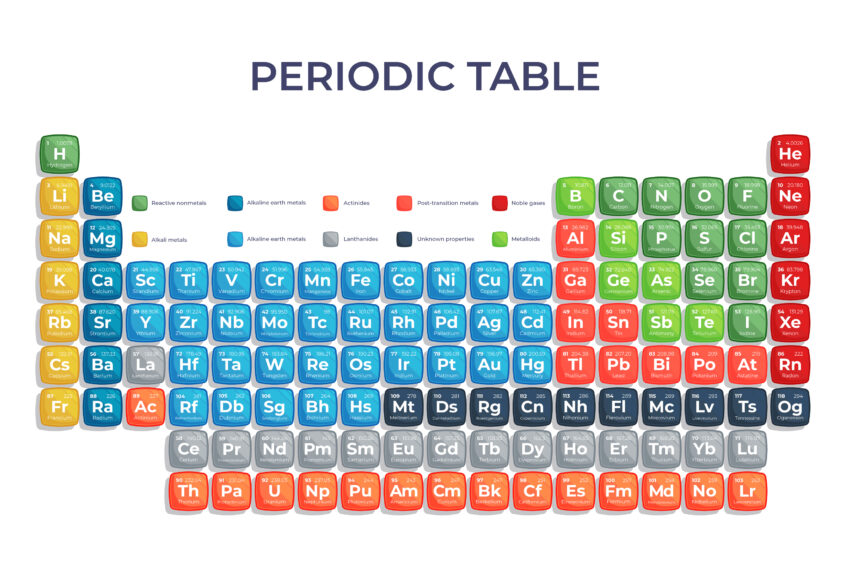
The periodic table is a core resource in chemistry, particularly for O-Level students. It serves as an organized framework, allowing learners to predict and understand the behavior of elements, essential for mastering various chemical concepts.
Let’s explore why the periodic table is crucial in O-level chemistry and how it aids the learning process.
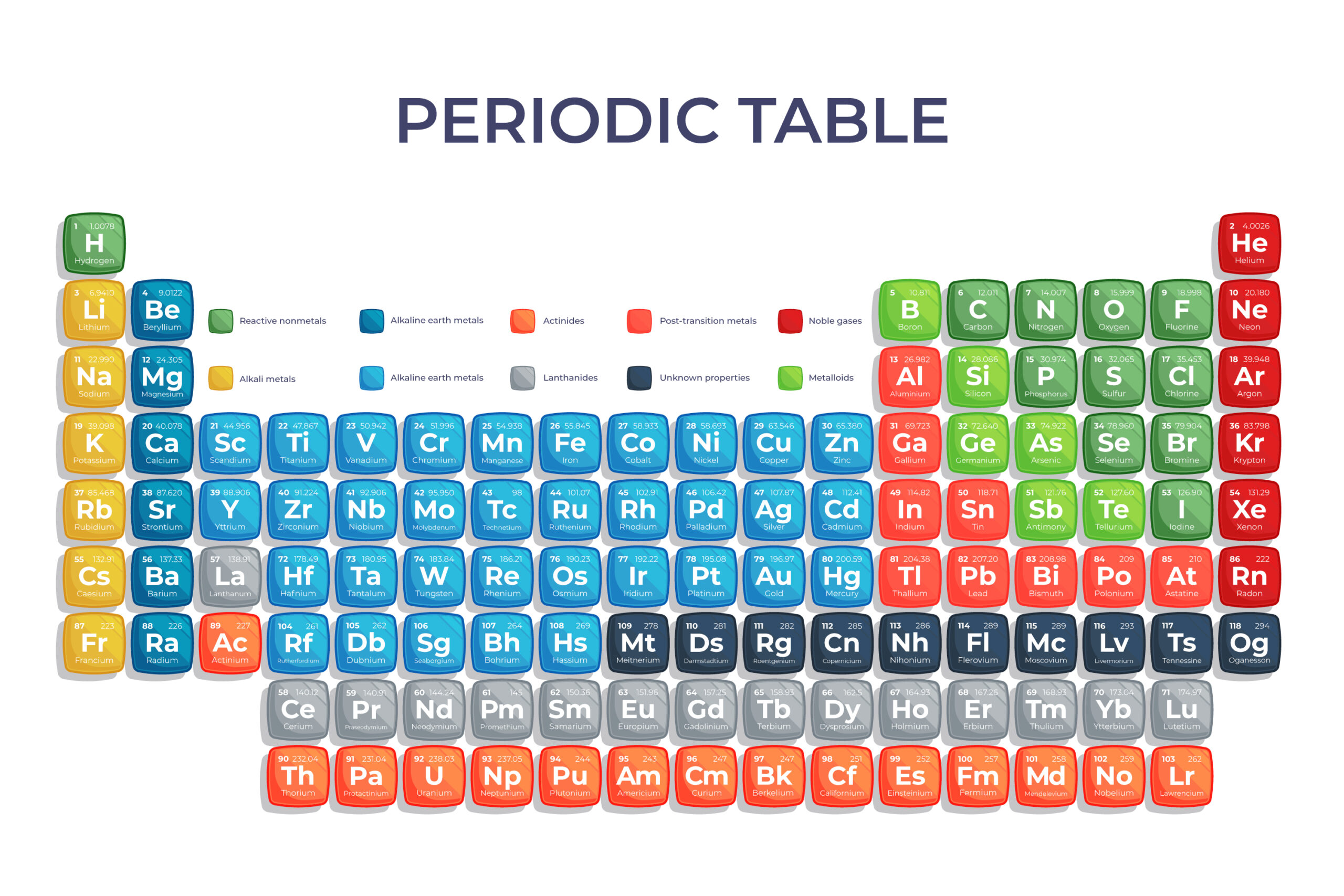
Why Is the Periodic Table Important in O-Level Chemistry?
The periodic table provides a structured overview of the elements—the basic building blocks of matter. For O-Level students, it serves as a roadmap to understanding chemical reactions, element properties, and trends that help explain why substances behave the way they do.
Historical Background
The periodic table has a rich history, with major contributions from scientists like Dmitri Mendeleev and Julius Lothar Meyer in the 19th century. They noticed recurring patterns among elements, leading to the development of the periodic table we use today. Mendeleev’s work, in particular, was groundbreaking in organizing elements based on their atomic masses and predicting undiscovered ones.
Structure of the Periodic Table
The periodic table consists of rows called periods and columns known as groups. Each element is represented by a unique symbol, with its position revealing valuable information about its atomic structure, properties, and behavior. This systematic arrangement helps students quickly identify and compare elements with similar characteristics.
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass
Every element has an atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. The atomic number determines an element’s identity and its position in the table. Meanwhile, atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons in an atom, and this information is crucial for understanding the periodic table’s structure.
Groups and Periods
- Groups (vertical columns) contain elements with similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. This similarity helps predict how elements will react chemically.
- Periods (horizontal rows) reflect the energy levels of the elements’ electrons. As you move across a period, the atomic number increases, and elements become less metallic.
Properties of Elements
The periodic table offers insights into the physical and chemical properties of elements. By understanding an element’s position, students can infer its state (solid, liquid, or gas), melting and boiling points, electronegativity, and more. This helps explain the behavior of elements in various reactions.
Trends in the Periodic Table
Several trends emerge from the periodic table, including:
- Atomic size: Decreases across a period and increases down a group.
- Ionization energy: The energy required to remove an electron increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electron affinity and electronegativity: These also exhibit predictable patterns that help explain how elements bond and react with each other.
Chemical Bonding
The periodic table is an essential tool for understanding chemical bonding. Elements in the same group tend to form similar bonds, making it easier for students to predict and explain bonding patterns. Understanding bonding is crucial for grasping how elements combine to form compounds.
Reactivity and Valency
An element’s reactivity is closely tied to its position on the periodic table. Elements with low ionization energy, such as those in Groups 1 and 2, are highly reactive. Valency—the ability of an element to form bonds—can also be deduced from its group number. This understanding is vital when balancing chemical equations and predicting chemical behavior.
Acids, Bases, and Salts
The periodic table helps students identify the elements involved in acids, bases, and salts. It provides insights into how these compounds react and what properties they possess, aiding in the understanding of chemical reactions, pH levels, and salt formation.
Transition Elements
The transition elements in the middle of the periodic table are unique in their ability to form multiple oxidation states and complex compounds. Their variable valency and the colorful compounds they form are central to various chemical processes, making them important for students to study.
Noble Gases
Group 18 contains the noble gases, which are known for their stability and lack of reactivity. These inert gases are important in studying chemical stability and applications like lighting and welding.
Importance in Chemical Reactions
The periodic table helps students predict chemical reactions, identify reactants and products, and balance chemical equations. By understanding the elements’ properties and trends, learners can master stoichiometry and comprehend the underlying principles of reactions.
Conclusion
For O-Level chemistry students, the periodic table is an indispensable tool. Its structured layout and wealth of information help students understand the behavior, properties, and interactions of elements. By utilizing it effectively, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and gain a strong foundation in chemistry.